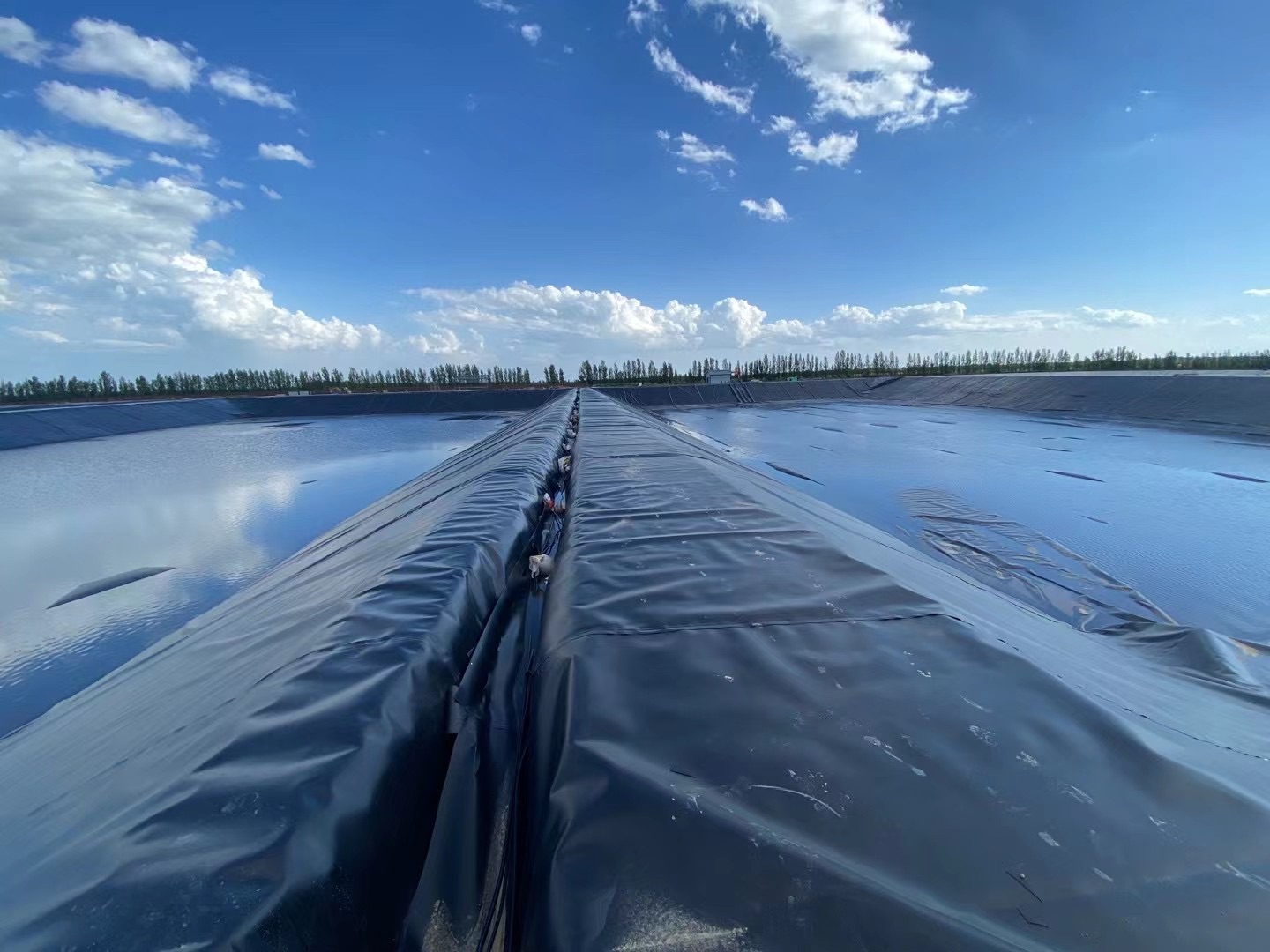
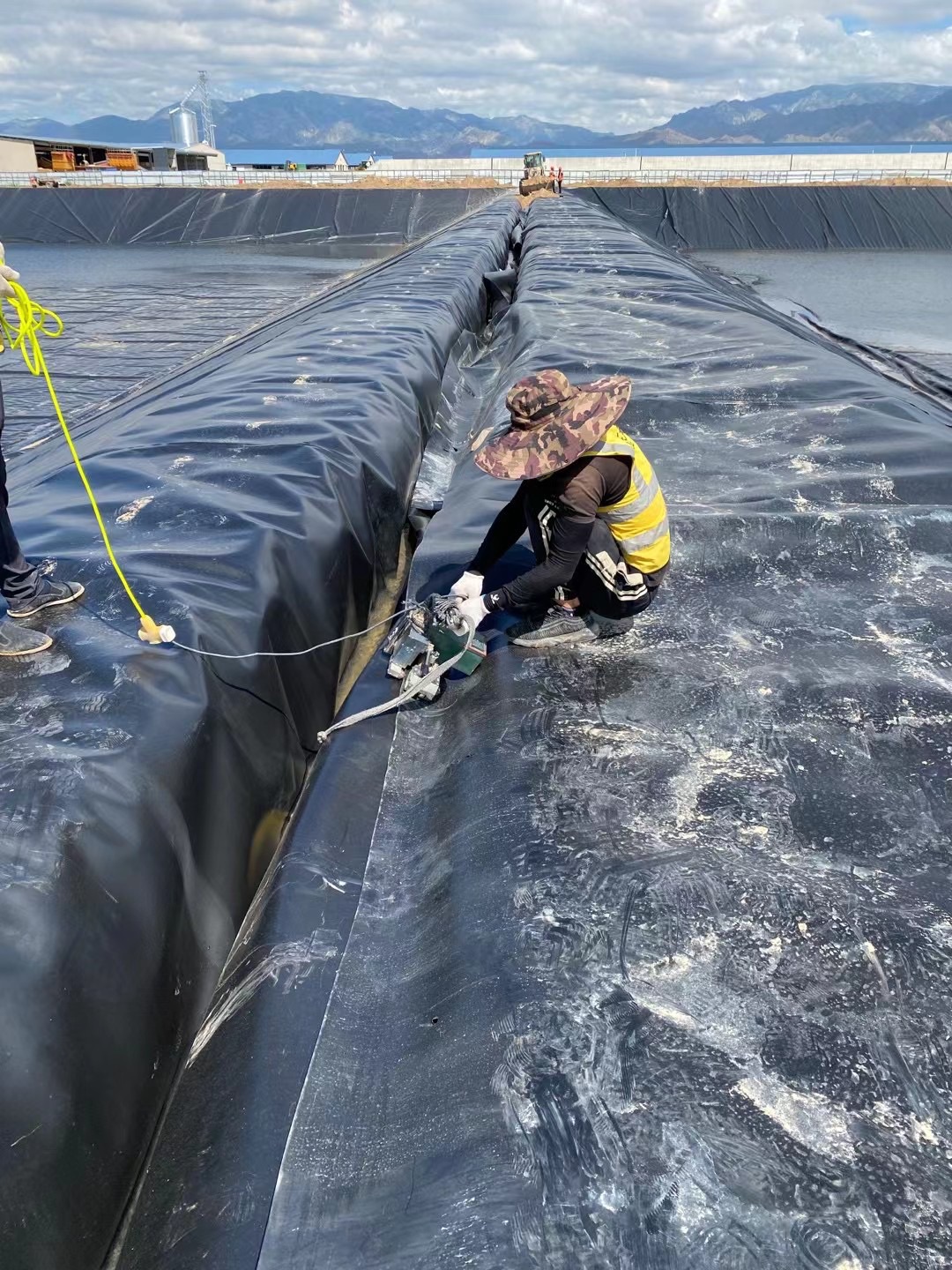
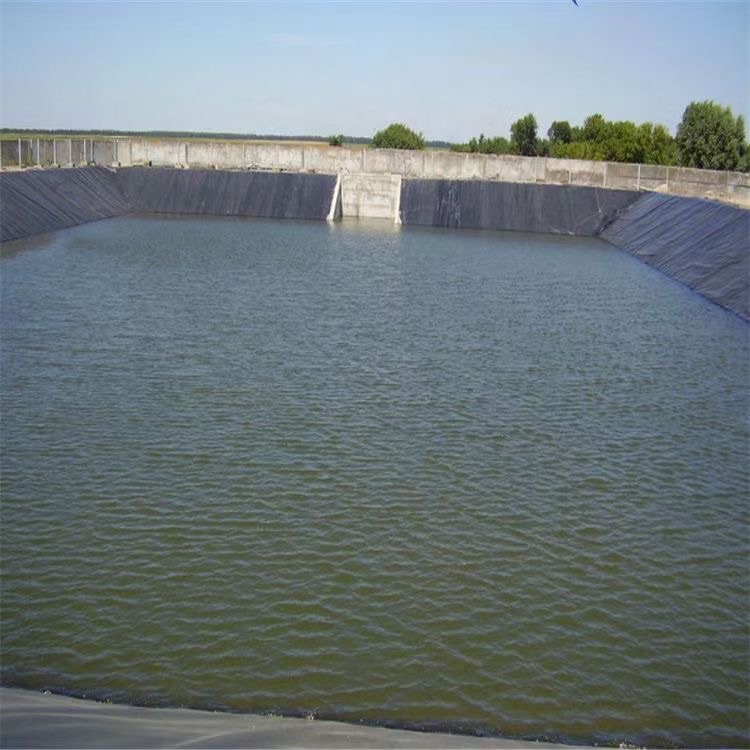
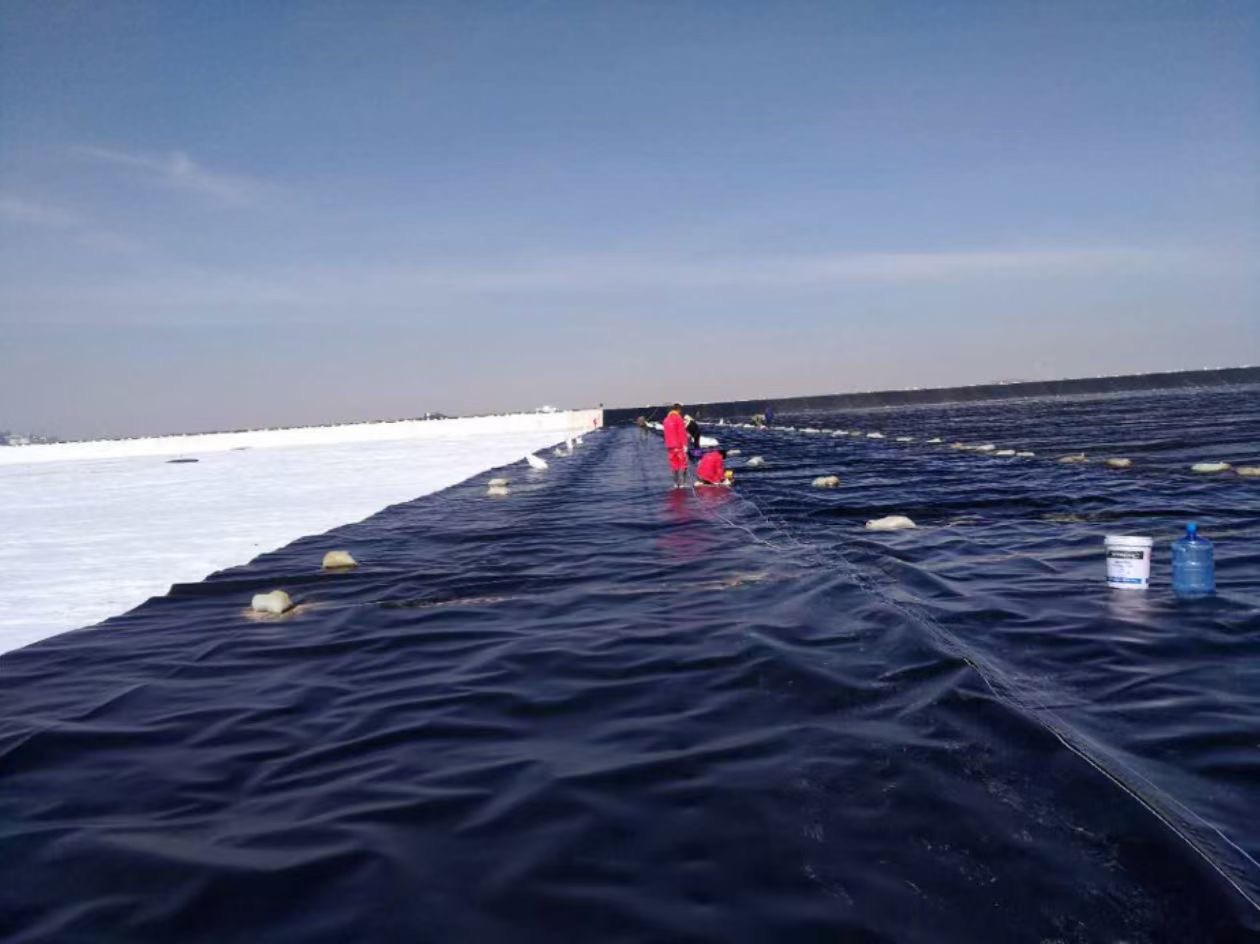
HDPE geomembrane pond liner for mining landfill dam fish pond
Product Features
HDPE geomembrane as a new material, it has excellent anti-seepage, anti-corrosion performance, good chemical stability, and it can be processed according to actual engineering needs. It has been widely used in dike, dam and reservoir anti-seepage of water conservancy projects, as well as in channels, reservoirs, sewage pools, swimming pools, buildings, underground buildings, landfill, environmental engineering, etc. HDPE geomembrane is used as anti-seepage, anti-corrosion, anti-leakage and moisture-proof material.
The HDPE geomembrane has different production standard, for example, American GRI GM standard, ASTM test method; and GB standard (China national standard).
1. Easy installation: as long as the pool is dug and leveled, no concrete cushion is needed;
2. Rapid installation: there is no solidification period required for structural concrete;
3. Resistance to foundation deformation: HDPE geomembrane can resist foundation settlement or foundation deformation due to its good fracture elongation;
4. Good effect: this is the biggest characteristic of HDPE geomembrane;
5. Recovery after useing: this is the biggest characteristic of HDPE geotextiles. After use, as long as it is put away and the pool is backfilled, it can be restored to its original state.
Product Parameters
|
HDPE Geomembrane ( GRI GM-13) |
|||||||||
| No. |
Test item |
Technical data |
|||||||
|
Thickness(mm) |
0.50 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 1.50 | 2.00 | 2.50 | 3.00 | |
| 1 | Density g/m2 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 | ≥0.94 |
| 2 | Tensile Yield Strength (MD&TD) (N/mm) | ≥8 | ≥11 | ≥15 | ≥18 | ≥22 | ≥29 | ≥37 | ≥44 |
| 3 | Tensile Breaking Strength (MD&TD) (N/mm) | ≥13 | ≥20 | ≥27 | ≥33 | ≥40 | ≥53 | ≥67 | ≥80 |
| 4 | Elongation at yield (MD&TD) (%) |
≥12 |
|||||||
| 5 | Elongation at break(MD&TD) (%) |
≥700 |
|||||||
| 6 | Tear Resistance (MD&TD) (N) | ≥58 | ≥93 | ≥125 | ≥160 | ≥190 | ≥250 | ≥315 | ≥375 |
| 7 | Puncture Strength (N) | ≥160 | ≥240 | ≥320 | ≥400 | ≥480 | ≥640 | ≥800 | ≥960 |
| 8 | Tensile load stress cracking (Constant load tensile method of incision) h |
≥300 |
|||||||
| 9 | Carbon Black Content (%) |
2.0-3.0 |
|||||||
| 10 | 85°C heat aging (Atmospheric OIT retention after 90d) (%) |
≥55 |
|||||||
| 11 | UV protection (OIT retention rate after 1600 h uviolizing) |
≥50 |
|||||||
| 12 | Carbon black dispersion |
In 10 datas, Grade 3≤1, Grade 4,5 are not allowed |
|||||||
|
13 |
Oxidative Induction Time (min) |
Atmospheric oxidative induction time≧100 |
|||||||
|
High pressure oxidative induction time≧400 |
|||||||||
Application and After-Sales Service
1. Landscape engineering: garage top greening, roof garden, football field, golf course, beach project.
2. Municipal engineering: road base, subway, tunnel, landfill.
3. Construction engineering: upper or bottom layer of building foundation, basement wall, bedding filtration and heat insulation.
4. Traffic engineering: highway, railway basement, dam and slope.
Installation
1. Environmental protection and sanitation (e.g. landfill, sewage treatment, poisonous and harmful substance treatment plant, dangerous goods warehouse, industrial waste, construction and blasting waste, etc.)
2. Water Conservancy (such as seepage prevention, leak plugging, reinforcement, seepage prevention vertical core wall of canals, slope protection, etc.
3. Municipal works (subway, underground works of buildings and roof cisterns, seepage prevention of roof gardens, lining of sewage pipes, etc.)
4. Garden (artificial lake, pond, golf course pond bottom lining, slope protection, etc.)
5. Petrochemical (chemical plant, refinery, gas station tank seepage control, chemical reaction tank, sedimentation tank lining, secondary lining, etc.)
6. Mining industry (bottom lining impermeability of washing pond, heap leaching pond, ash yard, dissolution pond, sedimentation pond, heap yard, tailings pond, etc.)
7. Agriculture (seepage control of reservoirs, drinking ponds, storage ponds and irrigation systems)
8. Aquaculture (lining of fish pond, shrimp pond, slope protection of sea cucumber circle, etc.)
9. Salt Industry (Salt Crystallization Pool, Brine Pool Cover, Salt geomembrane, Salt Pool geomembrane)